Contact
Taipei
TEL:+886-2-2557-5607
Taichung
TEL:+886-4-2320-2793
Shanghai
TEL:+86 21-6090-4391
Shenzhen
TEL:+86 755-83176807
North-east Asia Company
With the development of globalization, an increasing number of foreign companies are planning to establish their presence in Japan to meet their business or investment needs. Japan has always been a popular destination, and the local government welcomes the entry of foreign companies.
However, setting up a foreign-owned company in Japan requires compliance with legal procedures and corporate management requirements, as well as facing cultural differences and market competition. Nevertheless, establishing a successful foreign-owned company can bring many business opportunities and opportunities for growth.
I.Japanese company type
- When establishing a company in Japan, companies are divided into four types according to the Company Law: “joint stock company”, “limited liability company”, “partnership company” and “joint venture company”. Therefore, it is necessary to determine what type of company to establish. Foreigners generally set up corporations (joint-stock companies) and contract companies (limited liability companies) with relatively simple procedures.
- Kabushiki Kaisha: A company (joint-stock company) refers to a company that refers to investors at the time of establishment and capital increase as “shareholders” and delivers “shares” corresponding to the amount of investment to such shareholders to raise capital (working capital) .
A characteristic of a corporation is the “separation of investors and operators.” Shareholders raise funds under limited liability, and operators entrusted by shareholders conduct business operations and distribute benefits to shareholders. Of course, there is no legal problem with the investor-cum-operator of the company.
Therefore, in Japanese small and medium-sized enterprises, there are many cases where the “shareholders” as investors and the “directors” as managers are the same person. The disadvantage of a limited company is that the establishment cost is higher than that of a contract club, and the company’s articles of association need to be certified. The advantage of a limited company is that it has higher external credit than a contract club, and it is easier to negotiate with banks for financing or negotiate with customers than a contract club.
- Godo Kaisha: The investors of a contract company are the “members”, which means both “investors” and “operators”. At this time, there is no need to go through the process of “selecting directors through a general meeting of shareholders” like a company does, and “investor = company manager.” This is the biggest difference from Co., Ltd. Basically “all members have equal voting rights in management”, so there is no concept of the number of voting rights mentioned by the company. Therefore, in the “Members’ Meeting” where important management matters are decided in a contract club, the resolution cannot be decided without the attendance and approval of all members.
Minimum capital
Number of funders
Tenure of directors
Contribution share transfer
Issue stock
Is it possible to switch between joint-stock companies and limited liability companies?
Profit and loss distribution
Pros
Cons
Joint-stock Company
At least 1 Japanese Yen
1 person or more
2 years in principle, up to 10 years
Free in principle
Allow
Allow Issue stock
Allow
Allow switch companies
Allocate according to the capital contribution
High trust Wide range of tax-saving options
Higher social insurance premiums
Limited Liability Company
At least 1 Japanese Yen
1 person or more
Indefinitely
Consent of all funders is required
Allow
Allow Issue stock
Forbid
Forbid change company
Stipulated in the bylaws
Low cost to set up
Not well known in Japan
II.Documents should be prepared for company establishment
The basics of setting up a company need to confirm the following information:
- Confirm company type
Confirm the type to be registered, such as joint-stock companies or limited liability companies.
- Club name (company name/trade name)
Basically, you are free to decide the name. However, it is necessary to confirm in advance that there is no similar business name with the Legal Affairs Bureau under the jurisdiction of the company’s location. When deciding on a “business name”, don’t just check the “Company Law”. Attention should also be paid to the Anti-Unfair Competition Law.
(1).Japanese characters (hiragana, katakana, kanji)
(2).English letters (uppercase or lowercase A~Z)
(3).Arabic numerals (0123456789)
- Determine the amount of capital
One of the main points to worry about when setting up a company is how much capital is required? In Japan, the capital needs to be actually in place, and the capital is regarded as “the company’s reputation” to the outside world. A company with a large amount of capital is considered a financially strong company. A newly established company is not well known in the outside world. In this case, the amount of capital has a direct role as a criterion for judgment.
1. If a business management visa is required, capital of more than 5 million yen is required.
2. Business contents that require approval may require capital, so please confirm in advance.
- Management items
A company cannot do anything that is not documented in the company’s articles of association. That is to say, even if it is a business that has not yet been executed when it is first established if it is possible to do it later, it needs to be explained in advance. At the end of the business purpose of the articles of association, “all businesses related to or incidental to the preceding paragraph” may be added.
- Number of shareholders, directors, and auditors at the time of establishment (directors and shareholders)
1. Sponsor (shareholder): 1.
The shareholder’s identity document, such as passport or residence card, if it is a legal person shareholder document, must be authenticated by the local embassy.
2. Directors: 2.
One of them is the representative director, and it is recommended to have at least one local director to facilitate the opening of a bank account in the future.
3. Supervisor (supervision): None.
- Articles of Association
The company’s articles of association need to be written to stipulate the company’s operating methods, business scope, board of directors operations and other details.
- Investor, director information, tenure, etc.
Identity documents such as passports or residence cards are required for directors and shareholders.
- Company location
If you are renting, please check the lease agreement to see if there is any “Company do not” statement. The registered address on the articles of association must include a minimum administrative division.
III.Japanese company setup procedure
In Japan, foreign capital can establish a company independently, but when a foreigner becomes a sole proprietor, he must meet the same conditions as when the company was established and obtain a business management visa.
- The amount of funds must be 5 million yen or more.
- In addition to the operator, there are at least two Japanese employees.
When a foreigner sets up a company in Japan, the general procedure is as follows:
- 1.Confirm the investment information for the establishment of the company.
- 2.Preparation and Certification of Articles of Incorporation
After the company’s articles of association are established, the company’s articles of association need to be certified, and the seal or signature certification must be certified by a notary unit.
- 3.Remittance of capital
Once the articles of incorporation have been approved, the funds must be transferred to the bank account established by the founders. The registered funds need to be transferred through the bank account established by the sponsor. If the originator is an individual, transfer it to a personal bank account. If it is a company, transfer it to the account in the name of the company.
A recurring problem is that it is difficult for overseas residents and short-term residents to open a personal account. However, thanks to a legal change in 2017, even overseas residents can use the capital. You can pay by the following three methods.
(1).Transfer to the Japanese account of the director/representative director at the time of establishment.
(2).If the founder or director is not a Japanese resident, it is also possible to transfer to the bank account of a third-party individual.
(3).An account at an overseas bank branch in Japan or at a Japanese bank branch overseas.
- 4.Apply for company registration after making documents
Prepare documents for registration. The types of documents to be created will vary depending on the type of company, such as application for registration, seal, articles of association, letter of decision, consent to employment, identity verification, proof of capital contribution…etc.
- 5.Notification and declaration from the tax bureau
After completing the registration procedures at the Legal Affairs Bureau, report to the tax authority where the company is located. Due to the various taxes and fees levied on the company, it is the most important procedure after the establishment of the company.
- 6.Notify the prefecture tax office/municipal office
After the notification to the tax bureau is completed, the prefecture tax bureau and the municipal office must be notified at the end.
- Note:
To obtain an Entrepreneur/Management Visa, the following conditions must be met: - The required capital amount is 5 million Japanese yen or more.
- In addition to the operator, there must be at least two Japanese employees.
IV.Basic corporate tax in Japan
- Taxes that corporations must declare include corporation tax, corporation inhabitant tax (prefectural tax/city tax), corporation business tax, consumption tax, etc. Generally, a company’s final tax return must be filed within two months of the end of the business year. The following are the main taxes for Japanese companies:
Corporate tax

Corporate tax is a national tax equivalent to income tax for corporations, using a progressive tax rate. All income sources are subject to taxation.
Local Corporation Tax

This is an additional tax levied based on the corporate tax amount, classified as a local tax.
One of the new national taxes

GST
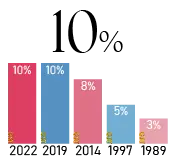
The tax rate increased from 8% to 10% in 2019. Consumption tax applies to nearly all goods and services.

Enterprise Tax
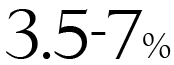
This is a local tax levied to support prefectural public services, with rates varying by region.
Prefecture Public Services

Inhabitant Tax
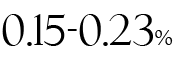
This is a local tax levied by municipal governments, including a corporate tax rate component and an equal portion based on company size.
The main all the various tax rates in Japan.
- Corporate Tax
Tax Calculation: Corporate Tax = Taxable Income × Corporate Tax Rate - Deductions
Small and Medium Enterprises (capital under 100 million yen):
• Net profit below 8 million yen: 15%.
• Net profit exceeding 8 million yen: 23.2%.
Large Enterprises (capital over 100 million yen): Unified tax rate of 23.2%.
- Local Corporation Tax
Tax Calculation: Corporate Tax × 10.3%.
Net profit below 8 million yen: 1.55%, Net profit exceeding 8 million yen: 2.39%.
- Consumption Tax(GST)
The tax rate increased from 8% to 10% in 2019. Consumption tax applies to nearly all goods and services. Exemption Conditions:Startups are exempt during the first two years if capital is below 10 million yen and the previous fiscal year's sales are under 10 million yen. Exceptions:
• (1).Taxable sales in the first half of the year exceed 10 million yen.
• (2).Total wages paid in the first half exceed 10 million yen.
Note: Consumption tax is collected from consumers, and companies must remit it even if operating at a loss.
- Enterprise Tax
This is a local tax levied to support prefectural public services, with rates varying by region. Tax Calculation: Enterprise Tax = Income × Enterprise Tax Rate Rates (Tokyo Example):
• Net profit below 4 million yen: 3.5%.
• Net profit between 4 million and 8 million yen: 5.3%.
• Net profit exceeding 8 million yen: 7%.
Only payable if the company generates profit.
- Inhabitant Tax
Rates:
1.Corporate Tax Rate Component:
Net profit below 8 million yen: 0.15%
Net profit exceeding 8 million yen: 0.23%.
2.Equal Portion: Based on company size, with a minimum of 70,000 yen. This applies to all companies, regardless of profitability.
Taxes are used for local infrastructure and public services. For companies operating less than a year, monthly calculations apply, with rates varying by locality.
V.Obtain a business management visa
Residence status becomes an important issue when a foreigner establishes a company in Japan and joins the management. Foreigners can carry out business and management activities by obtaining a business management visa. To obtain a business management visa, the following conditions must be met.
- Must have a business office in Japan (cannot be combined with a home).
- Employ 2 or more people who are permanently residing in Japan, or who pay 5 million yen or more per year in Japan.
- The capital is more than 5 million yen.
- Can demonstrate business stability and continuity.
Basically, it is difficult to obtain a business management visa without meeting these conditions.
-Notices-
- When a foreigner establishes a company in Japan and participates in its management, he or she must have the status of residence in Japan.
- You cannot start a business on a work visa or student visa. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain a business management visa.
- It is difficult to obtain a business management visa without a sizable business plan.
- It is recommended to find an experienced agency company to assist in providing the latest regulations and information on Japanese registered companies and provide relevant guidelines.
- Inter Area is a professional business service company, it has professionals who are familiar with business planning, registration, practical operation cases, related precautions and the latest information, providing customers with the most complete, fast and secure services.
Japan company set up Q&A
Q1. How long does it take to set up a Japan company?
- The time required to set up a company in Japan usually depends on the type of company and the completeness of document preparation. Generally, the process of setting up a company (KK) takes about 1-2 months, and opening a bank account requires an additional few weeks to complete.
Q2. Do you need a physical office address to set up your company?
- When setting up a company in Japan, you need to provide a registered address. This address does not have to be a physical office; a virtual office address can also be used as a registered company address, but must comply with local regulations.
Japan company set up Q&A
A:The time required to set up a company in Japan usually depends on the type of company and the completeness of document preparation. Generally, the process of setting up a company (KK) takes about 1-2 months, and opening a bank account requires an additional few weeks to complete.
A:When setting up a company in Japan, you need to provide a registered address. This address does not have to be a physical office; a virtual office address can also be used as a registered company address, but must comply with local regulations.
Related topics

オフショア会社(Offshore Company)は、海外法人としても知られており、OBU会社と呼ばれることもあります。一般的に、オフショア会社の登録地としてよく選ばれる場所には、英領バージン諸島(BVI)やサモア(Samoa)などがあります。オフショア会社を選ぶ際や運営する際には、まず各国の会社の特性を理解することが重要です…続きを読む >>
実際、オフショア会社の設立手続きはそれほど複雑ではなく、非常に迅速に行うことができます。しかし、重要なのは設立後の運用と維持管理であり、最新の法規制に準拠し、最も便利でコスト効率の良い方法で運営するためには、経験豊富な代行会社の支援を受けることをお勧めします。+886-2-2557-5607

Overseas companies are also called offshore companies, and some people call them OBU companies. Common places to register offshore companies are the B.V.I. and Samoa companies. As for how to choose and operate overseas companies, we should first understand the characteristics of companies in each country…Receive the best>>
In fact, the procedure for handling an offshore company is not complicated and is very fast. What is important is the subsequent operation and maintenance, how to comply with the latest policies and regulations, and operate in the most convenient and cost-effective way. It is recommended that companies still seek experienced agencies. +886-2-2557-5607

境外公司也称为离岸公司(Offshore Company),也有人称做OBU公司,常见注册离岸公司的地点如英属维京群岛BVI、萨摩亚Samoa公司。对于境外公司如何选择以及运作,首先应对各国公司特性有所了解…阅读更多>>
其实办理境外公司的程序并不复杂也十分迅速,重要的是后续的操作及维护,如何因应符合最新政策法规,以最便利并符合成本效益的方式运作,建议企业仍须寻求有经验的代办公司协助。
+886-2-2557-5607
境外公司也稱為離岸公司(Offshore Company),也有人稱做OBU公司,常見註冊離岸公司的地點如英屬維京群島BVI、薩摩亞Samoa公司。對於境外公司如何選擇以及運作,首先應對各國公司特性有所了解….閱讀更多>>
其實辦理境外公司的程序並不複雜也十分迅速,重要的是後續的操作及維護,如何因應符合最新政策法規,以最便利並符合成本效益的方式運作,建議企業仍須尋求有經驗的代辦公司協助。
+886-2-2557-5607

フィリピン政府は現在、外国投資家がフィリピンで株式会社、支店、または事務所を設立することを許可しており、ネガティブリストに含まれていないプロジェクトについては100%外資所有が可能です。
フィリピンに会社を設立する際、外資系企業の最低登録資本金額は20万米ドルです。小売業に関わる場合は、資本金額が50万米ドル以上必要です。また、資本金額は現地の実際のニーズに応じて調整可能です。続きを読む>>
フィリピンは英語圏の国ではありますが、その政策基準と各部門が確実に連携していないため、手続きの効率や書類がやや複雑です。さらに詳細な情報が必要な場合は、いつでもご連絡ください。 +886-2-2557-5607。

日本政府は、外国資本が日本で株式会社を設立することを許可しており、投資プロジェクトに対する特別な制限もありません。ただし、日本の会社設立には資本金を実際に注入する必要があるため、株主の資金をどのように調達し、どのように資金の流れを確保するかが、投資家が最も直面する困難です。資金の流れや銀行口座の開設を円滑にするためには、一般的に現地の住民またはパートナーを会社の株主として迎えることが推奨されます。これにより、初期の申請手続きをスムーズに進めることができます。
続きを読む >>
具体的な申請手続きについては、お気軽にご連絡ください。
+886-2-2557-5607
The Philippine government now allows foreign investors to set up joint stock companies, branches or offices in the Philippines. As long as the projects are not included in the negative list, they can be 100% wholly owned.When establishing a Philippine company, the minimum registered capital of a foreign-funded company is US$200,000; if a retail project is involved, it must be more than US$500,000; the capital amount can be allocated based on actual local needs. Receive the best>>
Although the Philippines is an English-speaking country, its policies and various departments are not really linked, so the work efficiency and documents are more complicated. For further relevant information, please contact us to confirm +886-2-2557-5607.
 The Japanese government allows foreign entities to establish limited liability companies (LLCs) in Japan, with no specific restrictions on investment projects.
The Japanese government allows foreign entities to establish limited liability companies (LLCs) in Japan, with no specific restrictions on investment projects.
However, since Japanese companies are required to have their registered capital actually paid in, the process of securing the funds from shareholders is a common challenge for investors.
To facilitate the flow of funds and the opening of bank accounts, it is generally recommended to have a local resident or partner as a company shareholder to streamline the initial application process.
Receive the best>>
For detailed application procedures, please feel free to contact us at +886-2-2557-5607
The Japanese government allows foreign entities to establish limited liability companies (LLCs) in Japan, with no specific restrictions on investment projects.
However, since Japanese companies are required to have their registered capital actually paid in, the process of securing the funds from shareholders is a common challenge for investors.
To facilitate the flow of funds and the opening of bank accounts, it is generally recommended to have a local resident or partner as a company shareholder to streamline the initial application process.
Receive the best>>
For detailed application procedures, please feel free to contact us at +886-2-2557-5607
菲律宾政府现已允许外国投资者菲律宾设立股份有限公司、分公司或办事处,只要是在负面清单以外的项目皆可100%独资。
设立菲律宾公司时,外资公司的最低登记注册资本额为20万美元;若是涉及零售项目则须50万美金以上;资本额并可依据当地实际需求到位。阅读更多>>
菲律宾虽为英语系国家,但其政策与各部门未能确实联动,因此办事效率与文件显得较为复杂,进一步相关资讯可与我们联系确认。
+886-2-2557-5607
日本政府准许外资在日本成立有限公司,对于投资项目也没有特别的限制。
不过因为日本公司的注册资金要求实际注资到位,因此股东资金如何到位的金流走向是投资者最常遇到的困难。为便利资金流以及银行帐户的开立,一般建议需要有当地的居民或是合伙人作为公司股东,以利前期的申请作业。阅读更多>>
具体申请细节,欢迎来电与我们联系。 +886-2-2557-5607

日本政府准許外資在日本成立有限公司,對於投資項目也沒有特別的限制。
不過因為日本公司的註冊資金要求實際注資到位,因此股東資金如何到位的金流走向是投資者最常遇到的困難。為便利資金流以及銀行帳戶的開立,一般建議需要有當地的居民或是合夥人作為公司股東,以利前期的申請作業。閱讀更多>>
具體申請細節,歡迎來電與我們聯繫。 +886-2-2557-5607

菲律賓政府現已允許外國投資者菲律賓設立股份有限公司、分公司或辦事處,只要是在負面清單以外的項目皆可100%獨資。
設立菲律賓公司時,外資公司的最低登記註冊資本額為20萬美元;若是涉及零售項目則須50萬美金以上;資本額並可依據當地實際需求到位。閱讀更多>>
菲律賓雖為英語系國家,但其政策與各部門未能確實聯動,因此辦事效率與文件顯得較為複雜,進一步相關資訊可與我們聯繫確認。
+886-2-2557-5607
 菲律宾政府现已允许外国投资者菲律宾设立股份有限公司、分公司或办事处,只要是在负面列表以外的项目皆可100%独资。
菲律宾政府现已允许外国投资者菲律宾设立股份有限公司、分公司或办事处,只要是在负面列表以外的项目皆可100%独资。
设立菲律宾公司时,外资公司的最低登记注册资本额为20万美元;若是涉及零售项目则须50万美金以上;资本额并可依据当地实际需求到位。閱讀更多>>
菲律宾虽为英语系国家,但其政策与各部门未能确实联动,因此办事效率与文件显得较为复杂,进一步相关信息可与我们联系确认 +886-2-2557-5607。
 菲律賓政府現已允許外國投資者菲律賓設立股份有限公司、分公司或辦事處,只要是在負面清單以外的項目皆可100%獨資。
菲律賓政府現已允許外國投資者菲律賓設立股份有限公司、分公司或辦事處,只要是在負面清單以外的項目皆可100%獨資。
設立菲律賓公司時,外資公司的最低登記註冊資本額為20萬美元;若是涉及零售項目則須50萬美金以上;資本額並可依據當地實際需求到位。閱讀更多>>
菲律賓雖為英語系國家,但其政策與各部門未能確實聯動,因此辦事效率與文件顯得較為複雜,進一步相關資訊可與我們聯繫確認 +886-2-2557-5607。
 フィリピン政府は現在、外国投資家がフィリピンで株式会社、支店、または事務所を設立することを許可しており、ネガティブリストに含まれていないプロジェクトについては100%外資所有が可能です。
フィリピン政府は現在、外国投資家がフィリピンで株式会社、支店、または事務所を設立することを許可しており、ネガティブリストに含まれていないプロジェクトについては100%外資所有が可能です。
フィリピンに会社を設立する際、外資系企業の最低登録資本金額は20万米ドルです。小売業に関わる場合は、資本金額が50万米ドル以上必要です。また、資本金額は現地の実際のニーズに応じて調整可能です。続きを読む>>
フィリピンは英語圏の国ではありますが、その政策基準と各部門が確実に連携していないため、手続きの効率や書類がやや複雑です。さらに詳細な情報が必要な場合は、いつでもご連絡ください。 +886-2-2557-5607。
 Under Taiwan’s tax regulations, if a Taiwanese tax resident holds more than 50% of the shares in a company located in a low-tax jurisdiction (with a tax rate of 14% or less) or has substantial control over such a company, and the annual earnings exceed NT 7 million, they must comply with the Individual Controlled Foreign Corporation (CFC) reporting requirements.
Under Taiwan’s tax regulations, if a Taiwanese tax resident holds more than 50% of the shares in a company located in a low-tax jurisdiction (with a tax rate of 14% or less) or has substantial control over such a company, and the annual earnings exceed NT 7 million, they must comply with the Individual Controlled Foreign Corporation (CFC) reporting requirements.
Regarding the CFC regime, we need to understand how to “defer taxation on earnings effectively,” how to “ensure autonomous and free movement of funds within legal frameworks,” and how to “enhance the allocation of resources across different countries.”
We should proactively diversify our planning to respond to the uncertainties of the environment. It is recommended to consult with experts to discuss your specific situation at +886-2-2557-5607, thoroughly evaluate your circumstances, and then make the most appropriate adjustments and plans.
 Singaporean banks allow foreign companies or individuals to open bank accounts in Singapore.
Singaporean banks allow foreign companies or individuals to open bank accounts in Singapore.
Personal Accounts: Generally, banks will require individuals to deposit the required minimum amount and provide proof of their source of funds.
Corporate Accounts: For foreign companies opening an offshore account in Singapore, banks will require sufficient documentation of overseas business activities and proof of the company’s operations to ensure the authenticity of the account user’s business. Read More>>
Different banks have their own conditions and rules, so it is crucial to research your options based on your situation. If you need further assistance, feel free to contact the Inter Area manager at +886-2-2557-5607.

台湾の税務居住者が海外において、低税負担国(税率14%以下)の会社の株式を50%以上保有している場合、または実質的な支配能力を持っている場合、当該年度の利益が NT$700 万元を超えると、個人CFC(Controlled Foreign Company)の申告が必要です。
CFC制度に関して、私たちが理解すべきことは「利益の課税をどのように延期するか」、「合法的に資金の自由な管理をどのように実現するか」、「各国のリソースをどのように強化し、効果的に配分するか」。
私たちは、不確実な環境に備えるため、多角的な計画を立てることが重要です。状況に応じて最適な調整と計画を行うために、専門家と連絡し、詳しい評価を行うことをお勧めします。+886-2-2557-5607
日本政府は、外国資本が日本で株式会社を設立することを許可しており、投資プロジェクトに対する特別な制限もありません。ただし、日本の会社設立には資本金を実際に注入する必要があるため、株主の資金をどのように調達し、どのように資金の流れを確保するかが、投資家が最も直面する困難です。資金の流れや銀行口座の開設を円滑にするためには、一般的に現地の住民またはパートナーを会社の株主として迎えることが推奨されます。これにより、初期の申請手続きをスムーズに進めることができます。
続きを読む >>
具体的な申請手続きについては、お気軽にご連絡ください。
+886-2-2557-5607
シンガポールの銀行では、外国の企業または外国人が口座を開設することが許可されています。
個人口座:通常、銀行は個人に対して基本的な預金額の入金を求め、その資金の出所を証明する必要があります。
法人口座:外国企業がシンガポールでオフショア口座を開設する場合、銀行は海外のビジネス情報や会社の経営証明を十分に提供することを求めます。これは口座使用者のビジネスの真実性を確認するためです。各銀行にはそれぞれ異なる条件と規則がありますので、ご自身の状況に応じて選択肢を調査することが非常に重要です。
続きを読む >>
必要がある場合は、いつでも匯佳マネージャー(+886-2-2557-5607) にご連絡ください。

若台湾税务居民于海外持有境外低税负国家之公司股权50%以上,或具有实质控制能力,当年度盈余超过NT 700万元者,须配合申报个人CFC。
对于CFC制度,我们所要了解的是如何”推迟课税盈余效益化”?如何”合法基础上资金自主自由”?如何”加强各式各国资源端口分配”?
我们应当未雨绸缪多角化规划来应映环境情势的不确定性。建议与专家联系讨论 +886-2-2557-5607,详实评估自身情况,再做出最合适的调整与规划。
 日本政府准许外资在日本成立有限公司,对于投资项目也没有特别的限制。
日本政府准许外资在日本成立有限公司,对于投资项目也没有特别的限制。
不过因为日本公司的注册资金要求实际注资到位,因此股东资金如何到位的金流走向是投资者最常遇到的困难。
为便利资金流以及银行账户的开立,一般建议需要有当地的居民或是合伙人作为公司股东,以利前期的申请作业。
阅读更多>>
具体申请细节,欢迎来电与我们联系。+886-2-2557-5607
 新加坡银行准许外国公司或是外国人在新加坡开立银行账户。
新加坡银行准许外国公司或是外国人在新加坡开立银行账户。
个人账户:通常上来说,银行会要求个人存入要求的基本存款,并且需要证明其资金来源。
公司账户:外国公司开立的新加坡离岸账户,银行会要求需要提供足够的国外业务数据以及公司经营证明,确保账户使用者的业务真实性。阅读更多>>
不同的银行有自己的条件与规则,因此根据您的情况研究您的选择非常重要,若有进一步需要可随时与汇佳经理联系 +886-2-2557-5607。

若台灣稅務居民於海外持有境外低稅負國家之公司股權50%以上,或具有實質控制能力,當年度盈餘超過NT700萬元者,須配合申報個人CFC。
對於CFC制度,我們所要了解的是如何”延緩課稅盈餘效益化”?如何”合法基礎上資金自主自由”?如何”加強各式各國資源端口分配”?
我們應當未雨綢繆多角化規劃來應映環境情勢的不確定性。建議與專家聯繫討論+886-2-2557-5607,詳實評估自身情況,再做出最合適的調整與規劃。
 日本政府准許外資在日本成立有限公司,對於投資項目也沒有特別的限制。
日本政府准許外資在日本成立有限公司,對於投資項目也沒有特別的限制。
不過因為日本公司的註冊資金要求實際注資到位,因此股東資金如何到位的金流走向是投資者最常遇到的困難。
為便利資金流以及銀行帳戶的開立,一般建議需要有當地的居民或是合夥人作為公司股東,以利前期的申請作業。
閱讀更多>>
具體申請細節,歡迎來電與我們聯繫。 +886-2-2557-5607
 新加坡銀行准許外國公司或是外國人在新加坡開立銀行帳戶。
新加坡銀行准許外國公司或是外國人在新加坡開立銀行帳戶。
個人帳戶:通常上來說,銀行會要求個人存入要求的基本存款,並且需要證明其資金來源。
公司帳戶:外國公司開立的新加坡離岸帳戶,銀行會要求需要提供足夠的國外業務資料以及公司經營證明,確保帳戶使用者的業務真實性。閱讀更多>>
不同的銀行有自己的條件與規則,因此根據您的情況研究您的選擇非常重要,若有進一步需要可隨時與匯佳經理聯繫 +886-2-2557-5607。